What Should the Pressure Gauge Read on My Pool Caretaker System
Pressure Gauges are pressure measuring instruments. Pressure and Temperature are 2 very of import parameters for all chemical industries. So, pressure measurement is of utmost importance. In that location are various pressure measuring instruments available to perform this task. Pressure measurement basically means the analysis of the fluid forces that are imparted on a surface. Accuracy of pressure measuring instruments are very important for proper operational control. In this article, we will explore diverse pressure measuring devices or pressure level gauges used across industries.
What is Pressure?
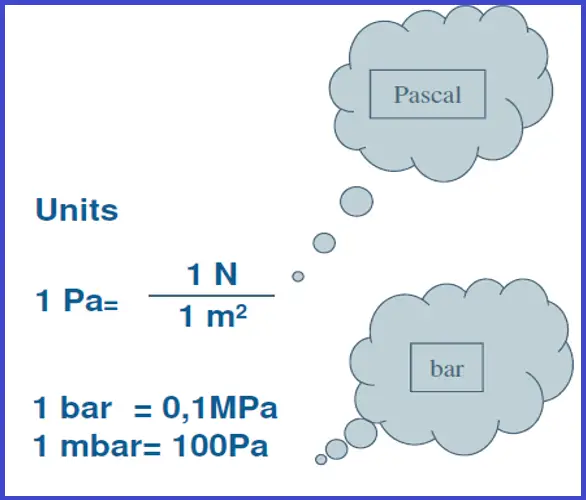
- Pressure level (P) is defined as Force (F) per Unit Area (A).
- The pressure is the activeness of one strength against some other force.
- The pressure is the force applied to or distributed over a surface.
- P = F/A F: Strength A: Expanse
Absolute pressure
- Measured higher up total vacuum or zilch absolute.
- Zero accented represents a total lack of pressure.
- Range: 0-1 Kg/cm^2 (a)/ 0-1 Bar (a)/ 0-760 mm Hg (a)
Atmospheric force per unit area: The pressure exerted by the globe's temper.
Barometric pressure: Same as Atmospheric pressure.
Vacuum Pressure: Pressure below atmospheric.
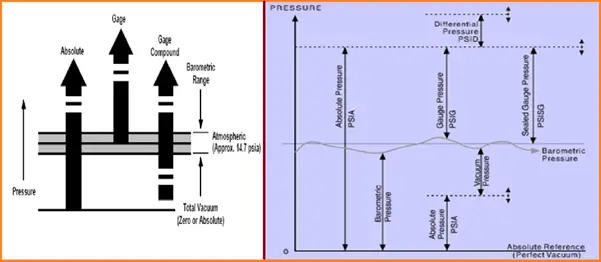
Differential pressure: It is the difference in pressure between ii points of measurements. In a sense, Absolute Pressure could exist considered as a differential pressure with a total vacuum or cipher absolute equally the reference.
Gauge/Gage pressure level: The pressure above atmospheric is gauge pressure. Represents a positive difference between measured and existing atmospheric force per unit area. For instance – Claret pressure.
Pressure Measurement
The measurement of pressure is considered the basic process variable for measurement of:-
- Period (departure of 2 pressures).
- Level (Head or backpressure).
- Temperature (Fluid pressure in a filled thermal system).
The Pressure Measurement Systems consist of two basic parts:-
- A main element, which is in contact, directly or indirectly, with the force per unit area medium and interacts with force per unit area changes.
- A secondary element, which translates this interaction into appropriate values for indicating, recording, and/or controlling.
Classification of Pressure Measuring Instruments or Pressure level Gauges
Pressure measuring devices can be classified on the basis of :
A: Force per unit area ranges:- Vacuum cuff, Draft gage, Depression range, compound cuff, Medium range, loftier range, etc..
B: Pattern principle involved in their operation:
- Mechanical movement of the sensing element – e.g. Bourdon gages, Diaphragm gages
- Electronic Sensors: e.g. Strain gages, Capacitive, Potentiometric, Resonant wire, Piezoelectric, Magnetic, Optical, etc.
C: On the basis of their application:
- Local pressure indication,
- Remote pressure indication,
- Corrosive service
- Pulsating service
- Differential pressure measurement
Methods of Pressure Measurement
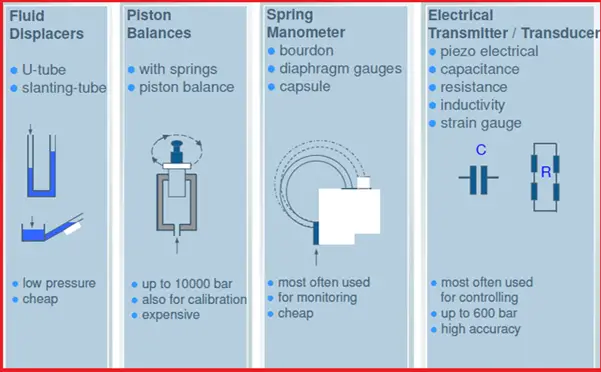
Basic Measurement – U Tube Manometer
A manometer is one of the oldest pressure measuring instruments and widely used even in recent times. Their functioning is simple and provides accurate results. As the proper noun suggests it is a "U" shaped tube fabricated of glass and partially filled with liquid.
The principle of the manometer is given as P= HEIGHT*DENSITY Where "P" is Pounds /sq. Inch; "Peak" in Inch " DENSITY" in pounds /Cu. Inch
Advantages of Manometer
- Fluids elementary & fourth dimension-proven
- Loftier accurateness & sensitivity
- Wide range of filling
Disadvantages of Manometer
- No over-range protection
- Big & bulky
- Measured fluids must be uniform with the manometer fluids
- Demand for leveling
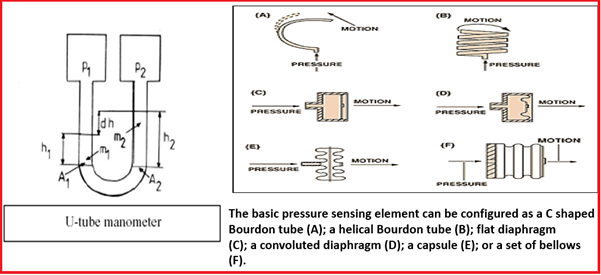
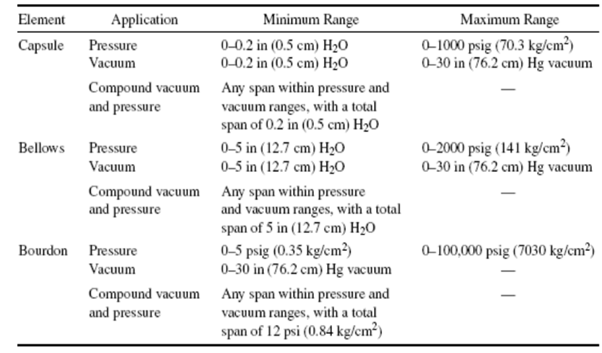
Pressure Sensing Elements
Pressure Sensing Elements are basically mechanical elements like plates, shells, and tubes. On the application of pressure, these elements deflect which is then converted into physical movement. They are a very important part of pressure measuring devices.
- The chief types of sensing elements are Bourdon tubes, diaphragms, capsules, and bellows.
- All the above devices, except diaphragms, provide a fairly large deportation. Mechanical gauges utilise that displacement which is further used by electrical sensors that crave a meaning movement.
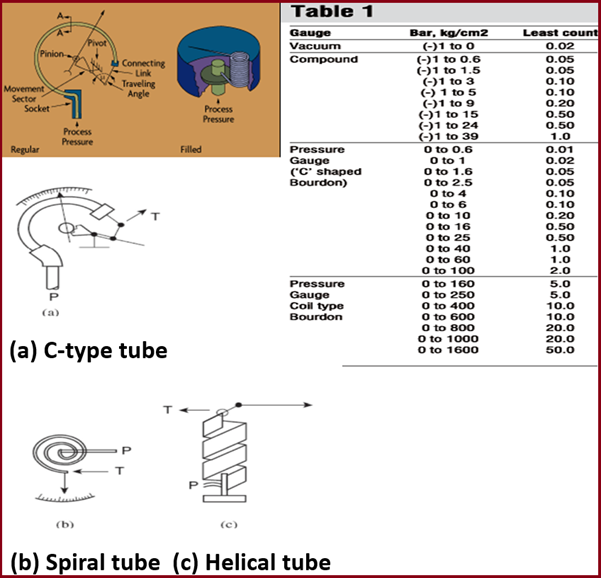
Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauges
The pressure level measuring device, Bourdon tube is the most mutual. They measure medium to high pressures. Bourdon tube is basically a curved tube with a round, coiled, or spiral shape.
- Information technology is the twisted tube whose cross-sectional isn't circular.
- Bourdon tubes types are c-type, helical blazon and spiral type.
- They should exist filled with oil to limit the impairment acquired by vibration.
- Range: (-)ane to 1600 Kg/cm^2
Advantages of Bourdon Tube
- Low cost & unproblematic structure
- Wide rangeability
- Good accuracy
- Adaptable to transducer designs
Disadvantages of Bourdon Tube
- Low spring gradient below 50psig
- Subject to Hysteresis
- Susceptible to shock & vibration
Bellows blazon Pressure level Guess
Bellows are as well used as a pressure level measuring instrument. Their main features are
- Fabricated of Bronze, S.S., BeCu, Monel, etc..
- The movement is proportional to a number of convolutions sensitivity is proportional to size.
- In full general, a bellows can discover a slightly lower pressure level than a diaphragm.
- The range is from 0-five mmHg to 0-2000 psi
- Accurateness in the range of 1% bridge
- It is a series of a circular parts so formed or joined that they can be expanded axially by pressure. A broad range of spring is employed to limit the travel of bellows.
- The measurement is express from .5 to seventy psi.
- It is greatly used as receiving elements for pneumatic recorders, indicators & controllers & also every bit a differential unit of flow measurement.
Advantages of Bellows Pressure Gauge
- High force delivered
- Moderate cost
- Good in the low to moderate pressure gauge
Disadvantages of Bellows Force per unit area Approximate
- Need ambient temperature pressure level compensation
- Crave spring for accurate characteristics
- Limited availability

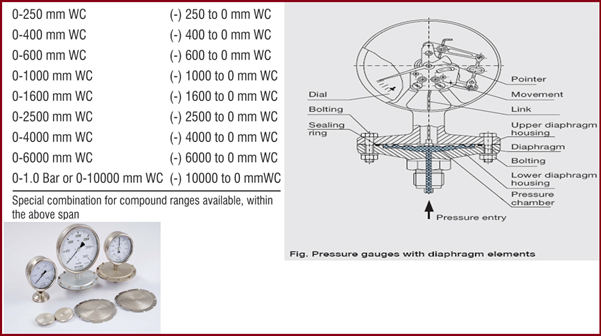
Diaphragm Pressure Estimate
The diaphragm tin be used to measure the force per unit area of both liquids and gases. 1 circular diaphragm is clamped between a pair of flanges to plant the force per unit area measuring element.
- The deflection of a flexible membrane is used for pressure measurement.
- For known pressures, the deflection is repeatable. Hence, calibration is possible.
- The pressure departure between its two faces dictates the deformation of a sparse diaphragm.
- The reference face up can exist open to the atmosphere to measure approximate pressure, open to a 2nd port to measure differential pressure, or can be sealed against a vacuum or other fixed reference pressure to mensurate absolute pressure. Mechanical, optical, or capacitive techniques are used to measure the deformation. Ceramic and metallic diaphragms are used.
- Range: (-) 10000 to (+) 10000 mm-WC
Advantages of Diaphragm pressure gauge
- Small size & moderate cost
- Linearity
- Adjustability to slurry services & accented & diff. press.
- High over range characteristics
Disadvantages of Diaphragm pressure estimate
- Limited to low pressure
- Difficult to repair
- Less vibration & shock resistance
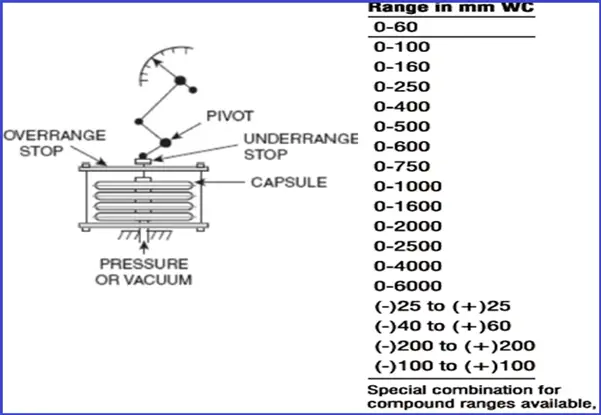
Capsule Force per unit area Approximate
Capsules as pressure measuring devices are used ordinarily for low pressure level applications.
- A sheathing is formed by joining the peripheries of ii diaphragms through soldering or welding.
- Used in some absolute pressure gages.
Range of Elastic-Element Pressure Gages
Pressure Measuring Accessories
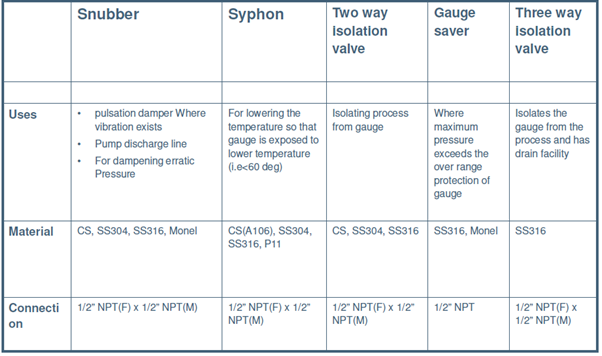
Diaphragm seals: These are designed to isolate the sensing element of pressure gauges from process fluids.
Judge Saver: Gauge Savers besides known as overpressure protectors are applicable where pressures exceed the maximum pressure rating of the force per unit area gauge.
Pulsation dampener: Dampeners considerably reduce the pulsations and make the guess reading easier and likewise improves the life of the gauge.
Siphon: This connection between the pressure level approximate & process in applications, where high temperatures like steam, vapors or fluids are present. It acts as a cooling coil and protects the estimate from loftier temperatures and as well helps in dissipating estrus.
Precautions: When outset installed the siphon should be filled with h2o or whatsoever other suitable dissever liquid.
- U Type – For Horizontal force per unit area tapping
- Q Type – For vertical pressure level tapping
Needle valve: The big round handle offers maximum ease and precise command to throttle the pressure level to the approximate.
Cake & Bleed Valve: Equipment Isolation with automatic pressure bleed for condom
Manifolds
- These are fluid distribution devices.
- These are used in conjunction with pressure gauges, differential pressure level gauges & differential pressure transmitters.
- They combine instrument isolation & equalizing in one block.
- The manifolds are available in 2way, three fashion & five-mode types with remote & directly mounting styles
Gauge cack: Information technology is used in conjunction with the siphon every bit an isolation valve. It is not recommended for force per unit area over 100 psi.

Few more than resources for you.
Understanding Pressure and Temperature in the context of Force per unit area Vessel Blueprint
Pressure Tests of Pipage systems-Hydrotest Vs Pneumatic Test
Temperature Measurement by Filled Thermal Systems
FUNDAMENTALS OF TEMPERATURE: An article
Few Points for High Temperature and High-Pressure Piping
Source: https://whatispiping.com/pressure-pressure-measuring-instruments-1/

0 Response to "What Should the Pressure Gauge Read on My Pool Caretaker System"
Post a Comment